/ News
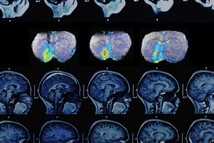
MRI sensor allows neuroscientists to map neural activity with molecular precision
An MRI sensor now allows neuroscientists to map neural activity with molecular precision. This is the first time anyone has been able to map neural signals with high precision over large brain regions in living animals, offering a new window on brain function, says the lead researcher. The new work focused on the study of the neurotransmitter dopamine in a region called the ventral striatum, which is involved in motivation, reward, and reinforcement of behavior.
Launched in 2013, the national BRAIN Initiative aims to revolutionize our understanding of cognition by mapping the activity of every neuron in the human brain, revealing how brain circuits interact to create memories, learn new skills, and interpret the world around us.
Before that can happen, neuroscientists need new tools that will let them probe the brain more deeply and in greater detail, says Alan Jasanoff, an MIT associate professor of biological engineering. "There's a general recognition that in order to understand the brain's processes in comprehensive detail, we need ways to monitor neural function deep in the brain with spatial, temporal, and functional precision," he says.
Jasanoff and colleagues have now taken a step toward that goal: They have established a technique that allows them to track neural communication in the brain over time, using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) along with a specialized molecular sensor. This is the first time anyone has been able to map neural signals with high precision over large brain regions in living animals, offering a new window on brain function, says Jasanoff, who is also an associate member of MIT's McGovern Institute for Brain Research.
His team used this molecular imaging approach, described in the May 1 online edition of Science, to study the neurotransmitter dopamine in a region called the ventral striatum, which is involved in motivation, reward, and reinforcement of behavior. In future studies, Jasanoff plans to combine dopamine imaging with functional MRI techniques that measure overall brain activity to gain a better understanding of how dopamine levels influence neural circuitry.
"We want to be able to relate dopamine signaling to other neural processes that are going on," Jasanoff says. "We can look at different types of stimuli and try to understand what dopamine is doing in different brain regions and relate it to other measures of brain function."
Tracking dopamine
Dopamine is one of many neurotransmitters that help neurons to communicate with each other over short distances. Much of the brain's dopamine is produced by a structure called the ventral tegmental area (VTA). This dopamine travels through the mesolimbic pathway to the ventral striatum, where it combines with sensory information from other parts of the brain to reinforce behavior and help the brain learn new tasks and motor functions. This circuit also plays a major role in addiction.
To track dopamine's role in neural communication, the researchers used an MRI sensor they had previously designed, consisting of an iron-containing protein that acts as a weak magnet. When the sensor binds to dopamine, its magnetic interactions with the surrounding tissue weaken, which dims the tissue's MRI signal. This allows the researchers to see where in the brain dopamine is being released. The researchers also developed an algorithm that lets them calculate the precise amount of dopamine present in each fraction of a cubic millimeter of the ventral striatum.
After delivering the MRI sensor to the ventral striatum of rats, Jasanoff's team electrically stimulated the mesolimbic pathway and was able to detect exactly where in the ventral striatum dopamine was released. An area known as the nucleus accumbens core, known to be one of the main targets of dopamine from the VTA, showed the highest levels. The researchers also saw that some dopamine is released in neighboring regions such as the ventral pallidum, which regulates motivation and emotions, and parts of the thalamus, which relays sensory and motor signals in the brain.
Each dopamine stimulation lasted for 16 seconds and the researchers took an MRI image every eight seconds, allowing them to track how dopamine levels changed as the neurotransmitter was released from cells and then disappeared. "We could divide up the map into different regions of interest and determine dynamics separately for each of those regions," Jasanoff says.
He and his colleagues plan to build on this work by expanding their studies to other parts of the brain, including the areas most affected by Parkinson's disease, which is caused by the death of dopamine-generating cells. Jasanoff's lab is also working on sensors to track other neurotransmitters, allowing them to study interactions between neurotransmitters during different tasks.
Source: http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/05/140501142233.htm
/ About us
Founded by Russian entrepreneur Dmitry Itskov in February 2011 with the participation of leading Russian specialists in the field of neural interfaces, robotics, artificial organs and systems.
The main goals of the 2045 Initiative: the creation and realization of a new strategy for the development of humanity which meets global civilization challenges; the creation of optimale conditions promoting the spiritual enlightenment of humanity; and the realization of a new futuristic reality based on 5 principles: high spirituality, high culture, high ethics, high science and high technologies.
The main science mega-project of the 2045 Initiative aims to create technologies enabling the transfer of a individual’s personality to a more advanced non-biological carrier, and extending life, including to the point of immortality. We devote particular attention to enabling the fullest possible dialogue between the world’s major spiritual traditions, science and society.
A large-scale transformation of humanity, comparable to some of the major spiritual and sci-tech revolutions in history, will require a new strategy. We believe this to be necessary to overcome existing crises, which threaten our planetary habitat and the continued existence of humanity as a species. With the 2045 Initiative, we hope to realize a new strategy for humanity's development, and in so doing, create a more productive, fulfilling, and satisfying future.
The "2045" team is working towards creating an international research center where leading scientists will be engaged in research and development in the fields of anthropomorphic robotics, living systems modeling and brain and consciousness modeling with the goal of transferring one’s individual consciousness to an artificial carrier and achieving cybernetic immortality.
An annual congress "The Global Future 2045" is organized by the Initiative to give platform for discussing mankind's evolutionary strategy based on technologies of cybernetic immortality as well as the possible impact of such technologies on global society, politics and economies of the future.
Future prospects of "2045" Initiative for society
2015-2020
The emergence and widespread use of affordable android "avatars" controlled by a "brain-computer" interface. Coupled with related technologies “avatars’ will give people a number of new features: ability to work in dangerous environments, perform rescue operations, travel in extreme situations etc.
Avatar components will be used in medicine for the rehabilitation of fully or partially disabled patients giving them prosthetic limbs or recover lost senses.
2020-2025
Creation of an autonomous life-support system for the human brain linked to a robot, ‘avatar’, will save people whose body is completely worn out or irreversibly damaged. Any patient with an intact brain will be able to return to a fully functioning bodily life. Such technologies will greatly enlarge the possibility of hybrid bio-electronic devices, thus creating a new IT revolution and will make all kinds of superimpositions of electronic and biological systems possible.
2030-2035
Creation of a computer model of the brain and human consciousness with the subsequent development of means to transfer individual consciousness onto an artificial carrier. This development will profoundly change the world, it will not only give everyone the possibility of cybernetic immortality but will also create a friendly artificial intelligence, expand human capabilities and provide opportunities for ordinary people to restore or modify their own brain multiple times. The final result at this stage can be a real revolution in the understanding of human nature that will completely change the human and technical prospects for humanity.
2045
This is the time when substance-independent minds will receive new bodies with capacities far exceeding those of ordinary humans. A new era for humanity will arrive! Changes will occur in all spheres of human activity – energy generation, transportation, politics, medicine, psychology, sciences, and so on.
Today it is hard to imagine a future when bodies consisting of nanorobots will become affordable and capable of taking any form. It is also hard to imagine body holograms featuring controlled matter. One thing is clear however: humanity, for the first time in its history, will make a fully managed evolutionary transition and eventually become a new species. Moreover, prerequisites for a large-scale expansion into outer space will be created as well.
Key elements of the project in the future
• International social movement
• social network immortal.me
• charitable foundation "Global Future 2045" (Foundation 2045)
• scientific research centre "Immortality"
• business incubator
• University of "Immortality"
• annual award for contribution to the realization of the project of "Immortality”.



 LinkedIn
LinkedIn
 LiveJournal
LiveJournal
 Google
Google
 Twitter
Twitter
 Facebook
Facebook
 Я.ру
Я.ру
 ВКонтакте
ВКонтакте
 Mail.ru
Mail.ru