/ News
Deep-learning algorithm predicts photos' memorability at "near-human" levels
Researchers from MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) have created an algorithm that can predict how memorable or forgettable an image is almost as accurately as humans—and they plan to turn it into an app that subtly tweaks photos to make them more memorable.
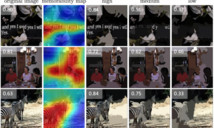
For each photo, the "MemNet" algorithm—which you can try out online by uploading your own photos—also creates a heat map that identifies exactly which parts of the image are most memorable.
"Understanding memorability can help us make systems to capture the most important information, or, conversely, to store information that humans will most likely forget," says CSAIL graduate student Aditya Khosla, who was lead author on a related paper. "It's like having an instant focus group that tells you how likely it is that someone will remember a visual message."
Team members picture a variety of potential applications, from improving the content of ads and social media posts, to developing more effective teaching resources, to creating your own personal "health-assistant" device to help you remember things.
Part of the project the team has also published the world's largest image-memorability dataset, LaMem. With 60,000 images, each annotated with detailed metadata about qualities such as popularity and emotional impact, LaMem is the team's effort to spur further research on what they say has often been an under-studied topic in computer vision.
The paper was co-written by CSAIL graduate student Akhil Raju, Professor Antonio Torralba, and principal research scientist Aude Oliva, who serves as senior investigator of the work. Khosla will present the paper in Chile this week at the International Conference on Computer Vision.
How it works
The team previously developed a similar algorithm for facial memorability. What's notable about the new one, besides the fact that it can now perform at near-human levels, is that it uses techniques from "deep-learning," a field of artificial intelligence that use systems called "neural networks" to teach computers to sift through massive amounts of data to find patterns all on their own.
Such techniques are what drive Apple's Siri, Google's auto-complete, and Facebook's photo-tagging, and what have spurred these tech giants to spend hundreds of millions of dollars on deep-learning startups.
"While deep-learning has propelled much progress in object recognition and scene understanding, predicting human memory has often been viewed as a higher-level cognitive process that computer scientists will never be able to tackle," Oliva says. "Well, we can, and we did!"
Neural networks work to correlate data without any human guidance on what the underlying causes or correlations might be. They are organized in layers of processing units that each perform random computations on the data in succession. As the network receives more data, it readjusts to produce more accurate predictions.
The team fed its algorithm tens of thousands of images from several different datasets, including LaMem and the scene-oriented SUN and Places (all of which were developed at CSAIL). The images had each received a "memorability score" based on the ability of human subjects to remember them in online experiments.
The team then pitted its algorithm against human subjects by having the model predicting how memorable a group of people would find a new never-before-seen image. It performed 30 percent better than existing algorithms and was within a few percentage points of the average human performance.
For each image, the algorithm produces a heat map showing which parts of the image are most memorable. By emphasizing different regions, they can potentially increase the image's memorability.
"CSAIL researchers have done such manipulations with faces, but I'm impressed that they have been able to extend it to generic images," says Alexei Efros, an associate professor of computer science at the University of California at Berkeley. "While you can somewhat easily change the appearance of a face by, say, making it more 'smiley,' it is significantly harder to generalize about all image types."
Looking ahead
The research also unexpectedly shed light on the nature of human memory. Khosla says he had wondered whether human subjects would remember everything if they were shown only the most memorable images.
"You might expect that people will acclimate and forget as many things as they did before, but our research suggests otherwise," he says. "This means that we could potentially improve people's memory if we present them with memorable images."
The team next plans to try to update the system to be able to predict the memory of a specific person, as well as to better tailor it for individual "expert industries" such as retail clothing and logo design.
"This sort of research gives us a better understanding of the visual information that people pay attention to," Efros says. "For marketers, movie-makers and other content creators, being able to model your mental state as you look at something is an exciting new direction to explore."
The work is supported by grants from the National Science Foundation, as well as the McGovern Institute Neurotechnology Program, the MIT Big Data Initiative at CSAIL, research awards from Google and Xerox, and a hardware donation from Nvidia.
Explore further: What makes an image memorable? We tend to remember pictures of people much better than wide open spaces
More information: memorability.csail.mit.edu/demo.html
Research paper: people.csail.mit.edu/khosla/papers/iccv2015_khosla.pdf
Provided by: Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Source: http://phys.org/news/2015-12-deep-learning-algorithm-photos-near-human.html
/ About us
Founded by Russian entrepreneur Dmitry Itskov in February 2011 with the participation of leading Russian specialists in the field of neural interfaces, robotics, artificial organs and systems.
The main goals of the 2045 Initiative: the creation and realization of a new strategy for the development of humanity which meets global civilization challenges; the creation of optimale conditions promoting the spiritual enlightenment of humanity; and the realization of a new futuristic reality based on 5 principles: high spirituality, high culture, high ethics, high science and high technologies.
The main science mega-project of the 2045 Initiative aims to create technologies enabling the transfer of a individual’s personality to a more advanced non-biological carrier, and extending life, including to the point of immortality. We devote particular attention to enabling the fullest possible dialogue between the world’s major spiritual traditions, science and society.
A large-scale transformation of humanity, comparable to some of the major spiritual and sci-tech revolutions in history, will require a new strategy. We believe this to be necessary to overcome existing crises, which threaten our planetary habitat and the continued existence of humanity as a species. With the 2045 Initiative, we hope to realize a new strategy for humanity's development, and in so doing, create a more productive, fulfilling, and satisfying future.
The "2045" team is working towards creating an international research center where leading scientists will be engaged in research and development in the fields of anthropomorphic robotics, living systems modeling and brain and consciousness modeling with the goal of transferring one’s individual consciousness to an artificial carrier and achieving cybernetic immortality.
An annual congress "The Global Future 2045" is organized by the Initiative to give platform for discussing mankind's evolutionary strategy based on technologies of cybernetic immortality as well as the possible impact of such technologies on global society, politics and economies of the future.
Future prospects of "2045" Initiative for society
2015-2020
The emergence and widespread use of affordable android "avatars" controlled by a "brain-computer" interface. Coupled with related technologies “avatars’ will give people a number of new features: ability to work in dangerous environments, perform rescue operations, travel in extreme situations etc.
Avatar components will be used in medicine for the rehabilitation of fully or partially disabled patients giving them prosthetic limbs or recover lost senses.
2020-2025
Creation of an autonomous life-support system for the human brain linked to a robot, ‘avatar’, will save people whose body is completely worn out or irreversibly damaged. Any patient with an intact brain will be able to return to a fully functioning bodily life. Such technologies will greatly enlarge the possibility of hybrid bio-electronic devices, thus creating a new IT revolution and will make all kinds of superimpositions of electronic and biological systems possible.
2030-2035
Creation of a computer model of the brain and human consciousness with the subsequent development of means to transfer individual consciousness onto an artificial carrier. This development will profoundly change the world, it will not only give everyone the possibility of cybernetic immortality but will also create a friendly artificial intelligence, expand human capabilities and provide opportunities for ordinary people to restore or modify their own brain multiple times. The final result at this stage can be a real revolution in the understanding of human nature that will completely change the human and technical prospects for humanity.
2045
This is the time when substance-independent minds will receive new bodies with capacities far exceeding those of ordinary humans. A new era for humanity will arrive! Changes will occur in all spheres of human activity – energy generation, transportation, politics, medicine, psychology, sciences, and so on.
Today it is hard to imagine a future when bodies consisting of nanorobots will become affordable and capable of taking any form. It is also hard to imagine body holograms featuring controlled matter. One thing is clear however: humanity, for the first time in its history, will make a fully managed evolutionary transition and eventually become a new species. Moreover, prerequisites for a large-scale expansion into outer space will be created as well.
Key elements of the project in the future
• International social movement
• social network immortal.me
• charitable foundation "Global Future 2045" (Foundation 2045)
• scientific research centre "Immortality"
• business incubator
• University of "Immortality"
• annual award for contribution to the realization of the project of "Immortality”.



 LinkedIn
LinkedIn
 LiveJournal
LiveJournal
 Google
Google
 Twitter
Twitter
 Facebook
Facebook
 Я.ру
Я.ру
 ВКонтакте
ВКонтакте
 Mail.ru
Mail.ru